Since March this year, a MapAction data scientist has been based at the Centre for Humanitarian Data in The Hague, supporting its workstream on predictive analytics. The aim of this important work is to forecast humanitarian emergencies and needs in order to trigger responses before a disaster occurs.
One of the projects the Centre’s predictive analytics team is working on, in partnership with the John Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory and individual country offices of the UN’s Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA), is the development of COVID-19 modelling tailored for each country’s specific context. This seeks to predict the scale, severity and duration of the outbreak within each country, including its likely effects on particularly vulnerable groups, such as people at risk of hunger or those using solid fuel indoors for cooking.
The project is also modelling the effects of non-pharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) such as curfews, travel bans and face masks, according to what is locally viable.
The inclusion of country-specific factors, looking at projections for specific vulnerable groups as well as the general population at a sub national level, can make this work particularly helpful for governments and humanitarian organisations to inform their COVID planning.
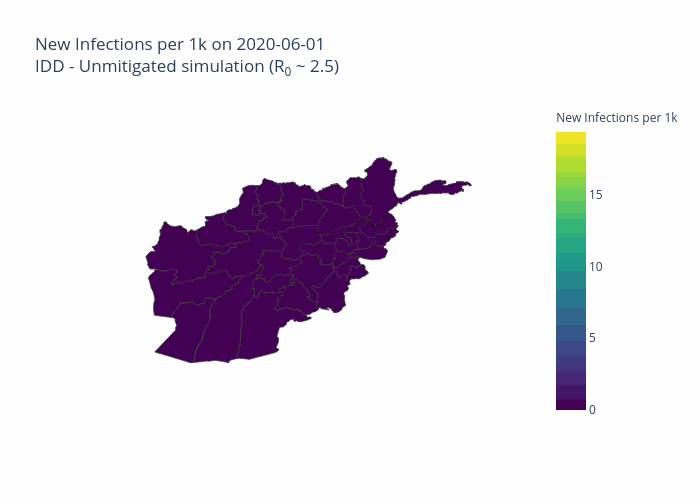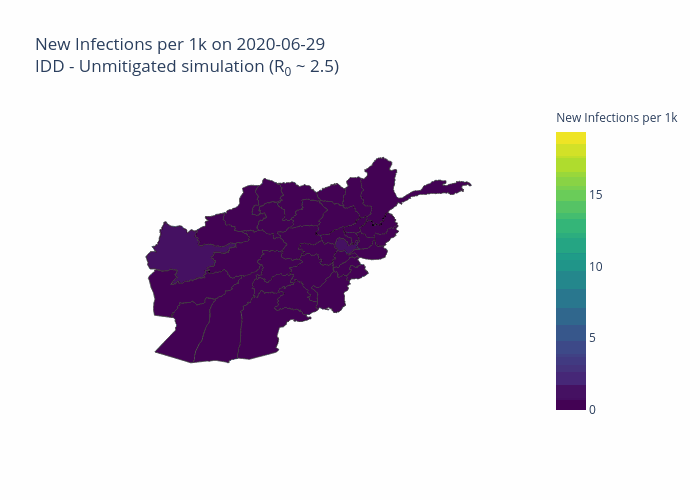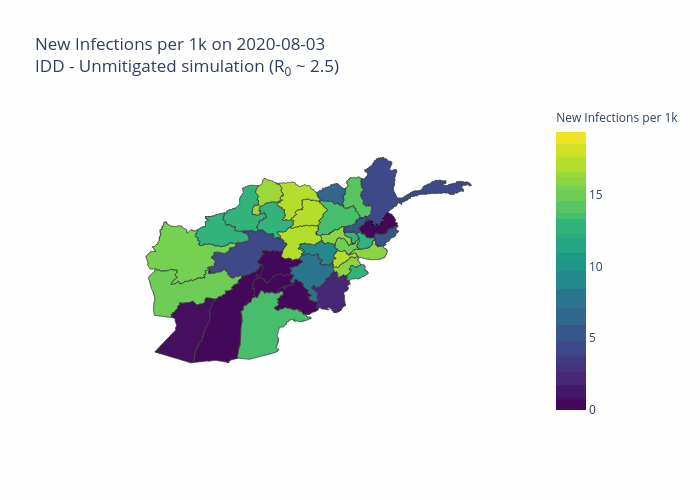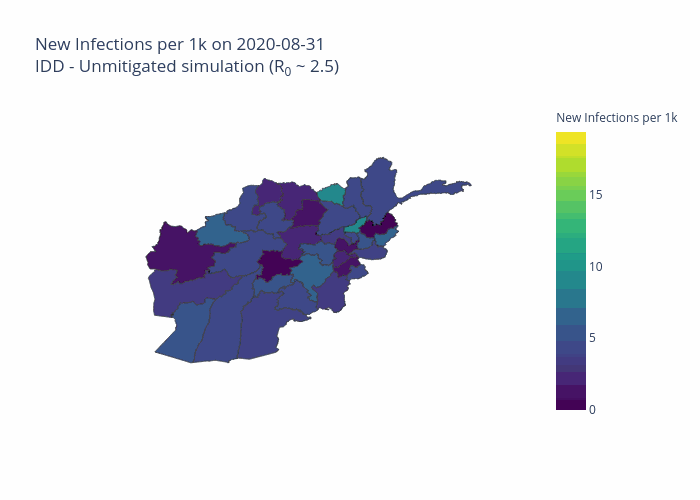

The initial model was developed for Afghanistan and is now being extended to other priority countries including the Democratic Republic of the Congo, South Sudan and Sudan.
We’re grateful for the support of the German Federal Foreign Office which funds MapAction’s data scientist role.
